
From weather station observations to forecast model data and advanced imagery, we have all your data needs covered. Our back-end collects and processes data from around the globe.
#Seasonality core manual mac#
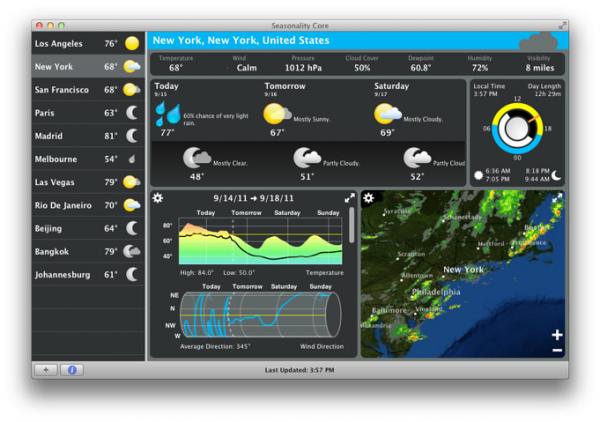
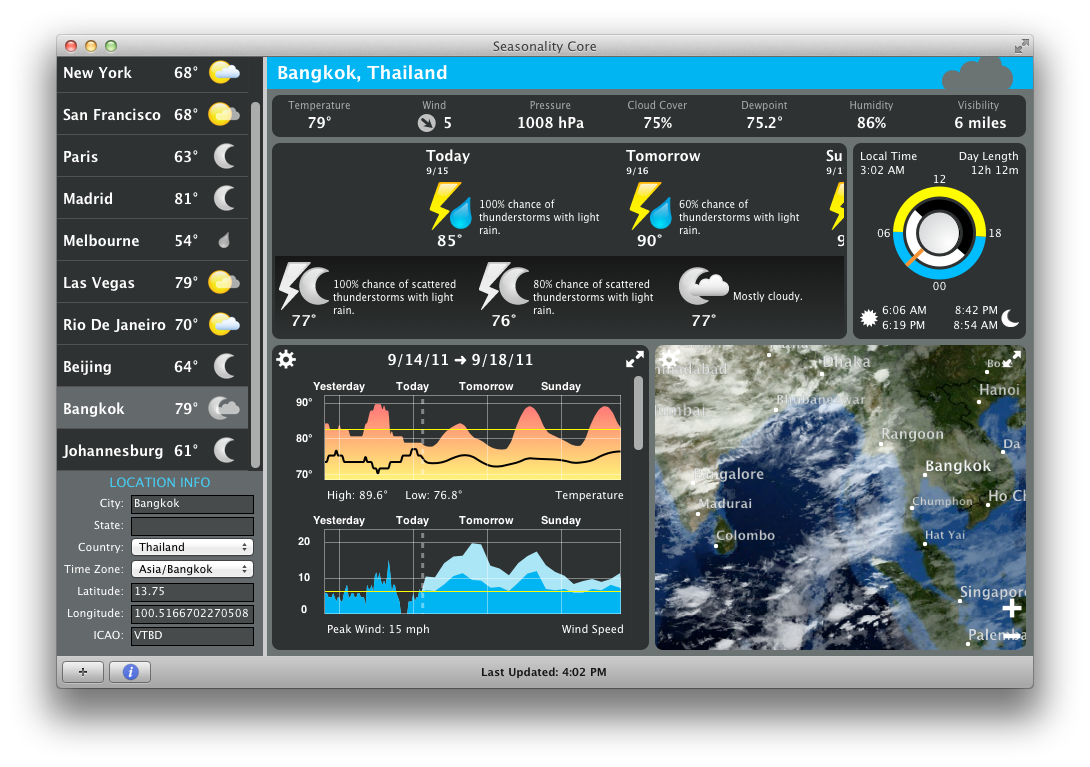
Otherwise, FALSE.Seasonality Core turns your Mac into an advanced home weather station, showing you the latest forecast, observations, and maps for locations worldwide. Attributes set for unit root, seasonality tests. Usage ATA.Seasonality(input, ppy, attr_set)Īssign from ATA.SeasAttr function. Suroot.test = 'correlogram' : this function is written based on M4 Competition Seasonality Test. Suroot.test = 'ocsb' : the Osborn-Chui-Smith-Birchenhall (1988) test is used (with null hypothesis that a seasonal unit root exists). Suroot.test = 'hegy' : the Hylleberg, Engle, Granger & Yoo (1990) test is used. Suroot.test = 'ch' : the Canova-Hansen (1995) test is used (with null hypothesis of deterministic seasonality) Suroot.test = 'seas' : a measure of seasonal strength is used, where differencing is selected if the seasonal strength (Wang, Smith & Hyndman, 2006) exceeds 0.64 (based on minimizing MASE when forecasting using auto.arima on M3 and M4 data).
#Seasonality core manual series#
Nsdiffs uses seasonal unit root tests to determine the number of seasonal differences required for time series to be made stationary. Then the test returns the least number of differences required to fail the test at the level uroot.alpha. In both of these cases, the null hypothesis is that x has a unit root against a stationary root alternative. Uroot.test = 'pp' : the Phillips-Perron test is used. Uroot.test = 'adf' : the Augmented Dickey-Fuller test is used. Then the test returns the least number of differences required to pass the test at the level uroot.alpha. Uroot.test = 'kpss' : the KPSS test is used with the null hypothesis that x has a stationary root against a unit-root alternative.
Ndiffs uses unit root tests to determine the number of differences required for time series to be made trend stationary. Ndiffs and nsdiffs functions to estimate the number of differences required to make a given time series stationary.
#Seasonality core manual manual#
Please review manual and vignette documents of latest forecast package. This function is a class of seasonality tests using corrgram_test from ATAforecasting package, ndiffs and nsdiffs functions from forecast package.Īlso, this function is modified version of ndiffs and nsdiffs written by Hyndman et al. Seasonality Tests for The ATAforecasting Description touristTR: Monthly number of tourists arrived in Turkey.fundingTR: Weekly Net Funding Level of Central Bank of Republic of.: Find Multi Frequency Using Spectral Density Of A Time Series.eq: Find Frequency Using Spectral Density Of A Time Series From.ATA.Transform: Transformation Techniques for The ATAforecasting.ATA.Shift_Mat: Lag/Lead (Shift) Function for Multivariate Series.ATA.Shift: Lag/Lead (Shift) Function for Univariate Series.

ATA.Core: The core algorithm of the ATA Method.ATA.CI: Confidence Interval function for the ATA Method.ATA.BoxCoxAttr: The ATA.BoxCoxAttr function works with many different types.ATA.BackTransform: Back Transformation Techniques for The ATAforecasting.ATA.Accuracy: Accuracy Measures for The ATAforecasting.ATA: Automatic Time Series Analysis and Forecasting using Ata.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
